|
Teeth: Incisors & Canines for cutting and tearing food, Molars to mash (pulverize) food.
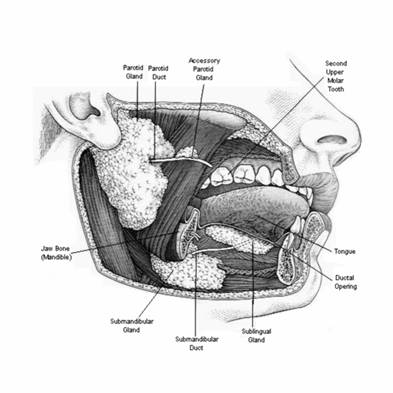
Salivary Glands: (1.5L Saliva per day, ≈7.0 Ph, 8.0 Ph during active secretion):
a. Submandibular glands, 70% of saliva (serous-mucous) b. Sublingual glands, 5% of saliva (mucous) c. Parotid glands, 20% of saliva (serous) d. Minor glands, 5% of saliva
Click on picture to enlarge
a. Slow Flow: isotonic → Na & Cl reabsorbed, K & Bi Carbonate (HCo3) Secreted in duct → hypotonic secretion. b. High Flow: Saliva osmolality approaches that of the plasma.
a. Ease swallowing. b. Maintain mouth moisture. c. Dissolves taste stimulating molecules. d. Initiates starch digestion. e. Keeps teeth clean. f. Neutralizes any reflux gastric acid due to its alkalinity.
a. ∂-amylase (ptyalin) stimulates starch breakdown in mouth. b. Lingual lipase, glands on tongue, breaks fats down into fatty acids & monoglycerides.
*******************************************************to be continued a. Mucins b. Lysozymes c. Lactoferrin d. High praline proteins e. Immunoglobulin A (Ig A) f. Kallilrein
a. Parasympathetic innervation. b. Sympathetic innervation. c. Reflex innervation.
|